



 Location: Home > Services > ELISA Technical Services
Location: Home > Services > ELISA Technical Services
Service process
1. Different detection ranges
The competition method is generally used to detect small molecule antigens that cannot bind to two antibodies at the same time; the sandwich method is suitable for the determination of divalent or more macromolecular antigens, but is not suitable for the determination of haptens and small molecule monovalent antigens because they cannot form a two-site sandwich.
2. Different detection principles
The detection principle of the competition method is: the antigen to be tested and the enzyme-labeled antigen compete for binding with the solid phase antibody, so the amount of enzyme-labeled antigen bound to the solid phase is inversely proportional to the amount of the antigen to be tested;
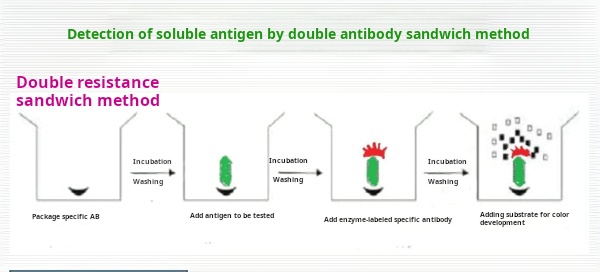
The detection principle of the sandwich method is: the macromolecular antigen is prepared into a solid phase antigen and an enzyme-labeled antigen conjugate respectively, and the double antigen sandwich method can be used to determine the antibody in the specimen. As long as the heterosexual antibody against the antigen to be tested is obtained, it can be used to coat the solid phase carrier and prepare the enzyme conjugate to establish this method.
3. Different detection steps
The operation steps of competitive detection are as follows:
(1) Connect the specific antibody to the solid phase carrier to form a solid phase antibody, and wash;
(2) Add a mixed solution of the sample to be tested and a certain amount of enzyme-labeled antigen to the test tube to react with the solid phase antibody. Only the enzyme-labeled antigen is added to the reference tube. After incubation, the combination of the enzyme-labeled antigen and the solid phase antibody can reach the most sufficient amount, and then wash;
(3) Add substrate to color: The reference tube has the most bound enzyme-labeled antigen, so the color is the darkest. The difference between the color depth of the reference tube and the color depth of the test tube represents the amount of antigen in the sample to be tested. The lighter the color of the test tube, the more antigen content in the sample;
(4) Detect the peak current of the culture system through square wave voltammetry, and finally determine the concentration of the final detection target of the system through the linear relationship between the peak current and the antigen-antibody.
The operating steps of the sandwich method are as follows:
(1) Connect the specific antibody to the solid phase carrier to form a solid phase antibody: wash to remove unbound antibodies and impurities;
(2) Add the sample to be tested: allow it to contact and react with the solid phase antibody for a period of time, allowing the antigen in the sample to bind to the antibody on the solid phase carrier to form a solid phase antigen complex. Wash to remove other unbound substances;
(3) Add enzyme-labeled antibody: allow the antigen on the solid phase immune complex to bind to the enzyme-labeled antibody. Thoroughly wash the unbound enzyme-labeled antibody. At this time, the amount of enzyme carried on the solid phase carrier is positively correlated with the amount of the sample to be tested;
(4) Add substrate: The enzyme in the sandwich complex catalyzes the substrate to become a colored product. The antigen is qualitatively or quantitatively determined based on the degree of color reaction.
Service characteristic
Service content
Customer provided
Delivery content
Online
Service
Online Service
08:30 - 17:30
Service
Hotline
800-880-8748
Customer service hotline
Scan
Wechat
 Scan wechat
Scan wechat